Here some tips to help how to design a better heat sink.
1. Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance refers to the sum of resistances to heat flow between the die and the coolant fluid. These heat flow resistances include the resistance between the die and the component casing, the resistance between the casing and the heat sink (thermal interface resistance), and the resistance between the heat sink and the fluid in motion. Thermal resistance does not factor non-uniform heat distribution and it is unsuitable for modeling systems that are not in thermal equilibrium.
Although the thermal resistance value is an approximation, it enables the modeling and analysis of thermal characteristics of semiconductor devices and heat sinks. Analyses of different heat sink designs are used to determine heat sink geometries and parameters that enable maximum heat dissipation. Complex modeling of thermal characteristics can be achieved by meshing heat sinks using 3D thermal resistances.
2. Material
Heat sinks are designed using materials that have high thermal conductivity such as aluminum alloys and copper. Copper offers excellent thermal conductivity, antimicrobial resistance, biofouling resistance, corrosion resistance, and heat absorption. Its properties make it an excellent material for heat sinks but it is more expensive and denser than aluminum.
Diamond offers a high thermal conductivity that makes it a suitable material for thermal applications. Its lattice vibrations account for its outstanding thermal conductivity. Composite materials such as AlSiC, Dymalloy, and copper-tungsten pseudo-alloy are also commonly used in thermal applications.
3.Heat Sink Fins: Electronics Cooling Efficiency
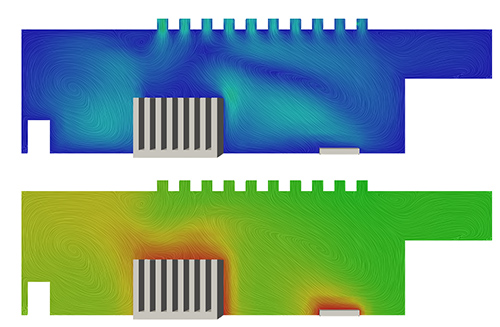
heat sink fins receive heat from an electronic device and dissipate it into the surrounding coolant fluid. The heat transferred by a fin to the coolant medium decreases as the distance from the base of the heat sink increases. Using a material that has a higher thermal conductivity and decreasing the aspect ratio of the fins help to boost the fins’ overall efficiency. The following image is part of the results of a simulation investigating the temperature characteristics of a heat sink design.
If you need any professional heat sink solution,please feel free to contact us


 +86-15220301231
+86-15220301231
 +8615220301231
+8615220301231
 jennyandcity
jennyandcity
 E-mail
E-mail
